Temperature Effects on Alnico Magnets
THE ORIGINAL ONLINE MAGNET COMPANY
Temperature Effects on Alnico magnets
Alnico magnets offer outstanding temperature stability. The output from Alnico magnets varies the least with changes in temperature, making it an ideal choice for temperature sensitive applications.
The reversible temperature coefficient of induction is -0.02%/deg C from ambient and the reversible temperature coefficient of Intrinsic Coercivity is +0.01%/deg C from ambient. This makes Alnico a perfect choice in performance critical applications such as medical and military. Increasing temperature may cause a degree of permanent loss in output from the Alnico but this depends on the physical shape of the Alnico magnet and the BH curve shape (the BH curve shape varies with temperature but the load line linking the magnet shape to the working point on the Intrinsic curve is shape dependent and is also independent of temperature. The loss through high temperature in Alnico may only be up to 5% but very high temperatures (over 530 deg C) may start to permanently alter the metallurgical structure of the Alnico which would cause a significant permanent and irreversible drop in output. Where high temperatures may be seen by the Alnico magnets, it is advised to heat the magnets to e.g. ten degrees or higher than the expected maximum so as to condition the Alnico magnets. This conditioning may cause a permanent drop in output but future thermal cycling to a temperature beneath the conditioning temperature will cause no further permanent drops in output (the only change in output would be the reversible losses that disappear as the magnet cools, as dictated by the temperature coefficients for Alnico).
It is recommended not to use Alnico magnets at temperatures above 525 or 550 deg C (550 deg C is 1022 deg F or 823 Kelvin). Alnico magnets are the only real choice for temperatures above 350 deg C as the Samarium in SmCo Rare Earth magnets migrates out of the structure above 350 deg C causing permanent loss in magnetic output.
-75 deg C is regarded as a reasonably acceptable lower temperature for Alnico although irreversible losses of around 10% are reported at -190 deg C but the actual losses are a function of the magnet geometry, total magnetic circuit and the BH curve shape.
The excellent temperature stability and massive upper temperature capability of Alnico makes it a superb magnet to use in aerospace, military and automotive sensor applications.
The way a magnet changes output with temperature variations is defined by its temperature coefficients.
The temperature coefficient of Intrinsic Coercivity (how Hci varies with temperature), b, for Alnico is approximately +0.01%/degree C for Alnico 5 (from ambient, but a range of -0.025%/degree C to +0.03%/degree C is possible depending on the Alnico grade) between +20 and +120 degrees C. Some grades, with positive coefficients actually increase their resistance to demagnetisation as they get hotter (albeit by a small amount per degree C rise in temperature from ambient).
The temperature coefficient of Remanent Induction (how Br varies with temperature), a, is -0.02%/degree C for Alnico 5 (from ambient, but a range of -0.035%/degree C to -0.025%/degree C is possible depending on the Alnico grade).
It should be noted that, strictly speaking, these values for a and b actually vary with temperature and use of stated values beyond 20 to 100 degrees C may result in inaccuracies when designing (actual BH curves at temperatures assist in clarifying for design purposes). But, as is quickly apparent, the variation in magnetic output over small temperature changes is minimal with Alnico.
Temperature characteristics of Alnico grades
|
MAGNET GRADE |
Rev.Temp.Coef. of Induction |
Rev.Temp.Coef. of Coercivity |
Max. Working Temperature |
|
(based on High working point) |
|||
|
Cast Alnico 2 |
-0.03 |
-0.02 |
450 ºC = 842 ºF |
|
Sintered Alnico 2 |
-0.035 |
-0.025 |
450 ºC = 842 ºF |
|
Cast Alnico 3 |
-0.035 |
-0.025 |
450 ºC = 842 ºF |
|
Sintered Alnico 3 |
-0.03 |
-0.025 |
450 ºC = 842 ºF |
|
Cast Alnico 5 |
-0.02 |
+0.01 |
525ºC = 977 ºF |
|
Sintered Alnico 5 |
-0.02 |
+0.01 |
525ºC = 977 ºF |
|
Cast Alnico 6 |
-0.02 |
+0.03 |
525ºC = 977 ºF |
|
Sintered Alnico 6 |
-0.02 |
+0.03 |
525ºC = 977 ºF |
|
Cast Alnico 5DG |
-0.02 |
+0.03 |
525ºC = 977 ºF |
|
Cast Alnico 5-7 |
-0.02 |
+0.03 |
525ºC = 977 ºF |
|
Cast Alnico 8 |
-0.025 |
+0.01 |
555ºC = 1022 ºF |
|
Sintered Alnico 8 |
-0.025 |
+0.01 |
555ºC = 1022 ºF |
|
Cast Alnico 8HC |
-0.025 |
+0.01 |
555ºC = 1022 ºF |
|
Sintered Alnico 8HC |
-0.025 |
+0.01 |
555ºC = 1022 ºF |
|
Cast Alnico 9 |
-0.025 |
+0.01 |
555ºC = 1022 ºF |
|
Sintered Alnico 9 |
-0.025 |
+0.01 |
555ºC = 1022 ºF |
Example BH curve for Alnico 5 (Alnico5_ACA44)
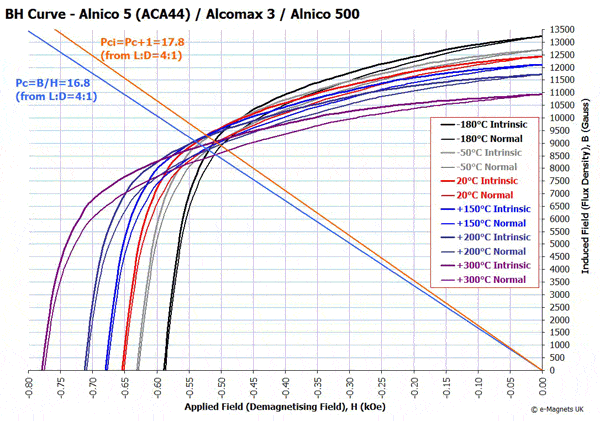
The way the magnetic output changes with temperature and how a magnet can be demagnetised by external magnetic fields is discussed in more detail on the NdFeB website (the information it gives can be equally applied to Alnico, taking into account the magnetic parameters given above).
Discover More
Get in touch today
Please do not hesitate to contact us with any question or query you may have. Our professional team will give you expert advice and guidance for your magnetic application and equipment.


