Bunting provides sintered Neodymium-Iron-Boron (NdFeB) magnets across a wide range of applications due to their excellent magnetic properties. These high energy magnets are often employed in devices such as medical mixers and stirrers, where their strong magnetic fields are crucial for efficient operation. However, these devices require sterilisation through both X-ray and Gamma-ray radiation. In this blogpost, we explore the effects of such radiation on the magnetic properties of sintered NdFeB magnets.

Radiation Sterilisation
Radiation sterilisation is a process that uses ionizing radiation to eliminate microorganisms. X-rays and gamma rays are particularly effective due to their high energy and deep penetration capabilities.
Radiation Effects on Neodymium Magnetic Properties
In order to support a customer with specific test data, Bunting conducted an extensive test programme to compare virgin magnets with different types of irradiated samples.
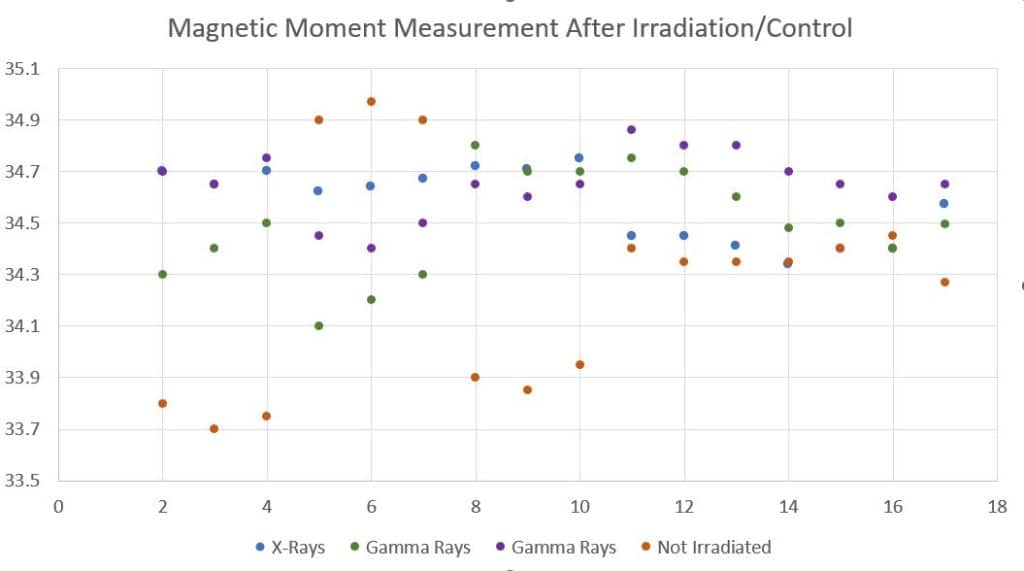
Generally, studies have shown that gamma radiation can cause changes in the magnetic properties of Neodymium Iron Boron (NdFeB) permanent magnets. The magnetic flux loss is generally around ±0.5%[1], which is relatively insignificant for most applications. This slight reduction is due to the radiation-induced defects in the crystal structure of the magnets, which can alter the alignment of magnetic domains.
Our testing was a direct comparison with these previous studies and demonstrated that the total magnetic moment variation over the test was only 5%. This includes the dimensional variation as well as magnetic material variation of the base magnet. The control study showed a similar variation of 5%.
In conclusion, the tests proved that the loss of magnetic performance of a NdFeB magnet from irradiation, at these levels, is so minor that it can be effectively discounted.
Application in Medical Mixing Devices
For medical mixing devices, the minimal changes in magnetic properties due to radiation are generally acceptable as the variation falls within the general specification of the material.
The benefits of using radiation sterilisation, including the effectiveness and non-thermal nature, outweigh the minor drawbacks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, whilst X-ray and gamma ray radiation can cause minor changes in a NdFeB magnet, by understanding and mitigating the effects of radiation it is possible to continue to leverage the superior magnetic properties of NdFeB magnets in advanced medical applications.
Bunting’s specialist magnet application engineering team provides technical support in understanding magnets and specific applications.
[1] Studying of the influence of Gamma radiation on magnetic properties of Sr, La, Co, Fe Ferrite Magnetic Materials, Giao, Dung, An and Hung
